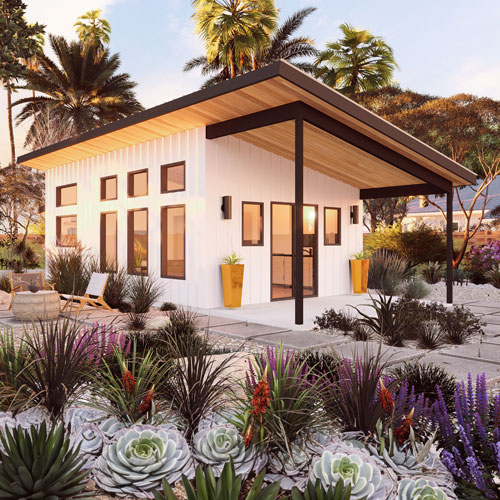
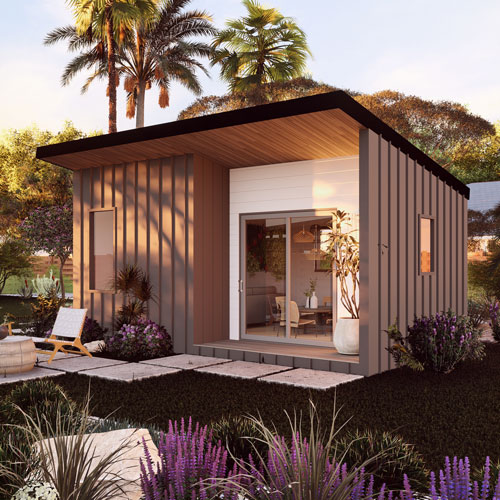
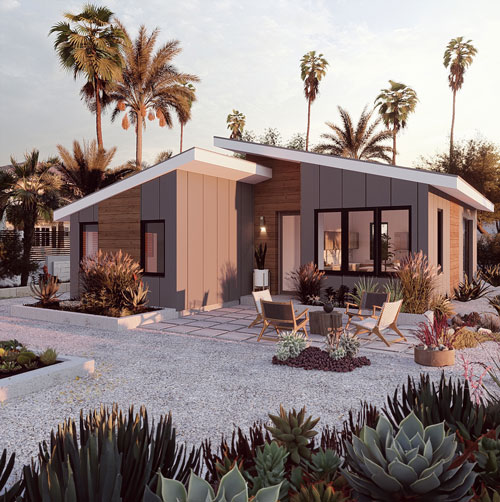
In the midst of a housing affordability crisis that grips many parts of the world, particularly in urban centers, Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) have emerged as a beacon of hope. These compact, efficient living spaces, known variously as granny flats, in-law units, or backyard cottages, offer a unique solution to the pressing need for affordable housing. This blog delves into the intriguing statistics and compelling facts that highlight the role of ADUs in contributing to affordable housing solutions.
The Cost-Effective Nature of ADUs
One of the most compelling aspects of ADUs is their cost-effectiveness. Unlike traditional housing options, ADUs do not require the purchase of additional land, a significant factor in the high cost of new housing developments. The elimination of major new infrastructure, structured parking, and elevators further reduces the financial barriers to creating new living spaces. This makes ADUs an affordable alternative, not just for potential renters, but also for homeowners looking to expand their living space or generate rental income.
The Impact on Housing Affordability
Studies and reports from various housing and urban planning organizations have shed light on the tangible impact of ADUs on the housing market. For instance, in California, a state that has been at the forefront of the ADU movement, legislation has been enacted to streamline the approval process for these units, recognizing their potential to alleviate the housing shortage. The result has been a significant increase in the number of ADUs being built, contributing to the stock of affordable housing without the need for large-scale new construction projects.
Financial Incentives and Support
To encourage the development of ADUs, many local governments and housing authorities have introduced financial incentives and support programs. These include grants, low-interest loans, and fee waivers, aimed at reducing the cost burden on homeowners. Such initiatives not only make it more feasible for homeowners to build ADUs but also ensure that these units can be rented out at more affordable rates, thereby contributing to the overall availability of lower-cost housing options.
Design and Innovation
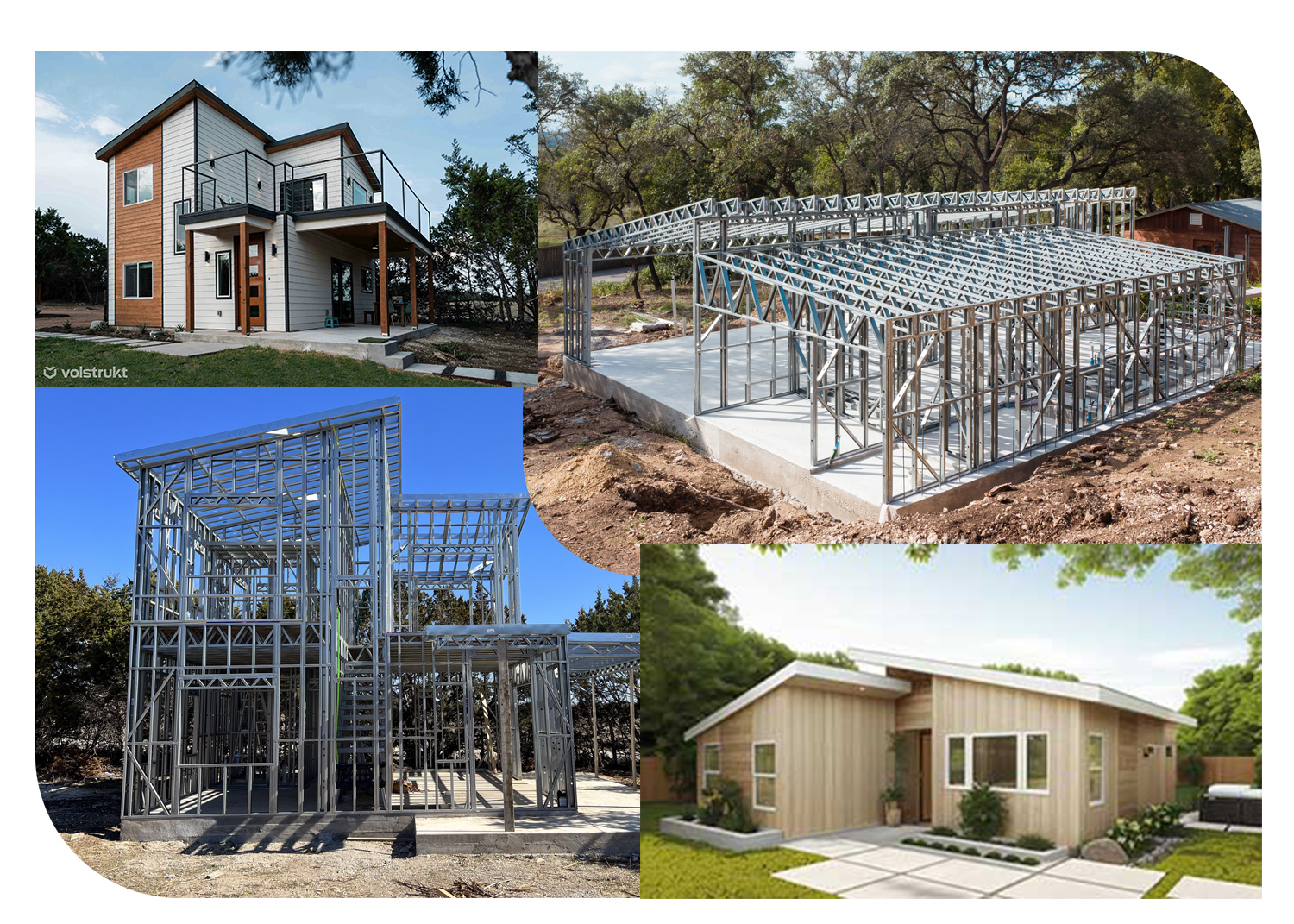
The rise of ADUs has also sparked innovation in housing design and construction. Compact living has encouraged architects and builders to think creatively about how to maximize space and efficiency in small footprints. This has led to the development of modular and prefab ADU models, which can be constructed off-site and installed quickly, further reducing costs and construction times.
Community and Environmental Benefits
Beyond their affordability, ADUs offer numerous community and environmental benefits. By increasing density in existing neighborhoods, ADUs can help reduce urban sprawl and its associated environmental impacts. They also support multi-generational living and can help keep communities intact by providing affordable housing options for young adults, seniors, and others on fixed incomes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, the development of ADUs is not without challenges. Zoning regulations, neighborhood resistance, and financing hurdles can still pose obstacles. However, the growing recognition of ADUs' potential to contribute to affordable housing solutions is leading to ongoing policy reforms and increased support for homeowners and developers interested in pursuing this path.
Conclusion
ADUs represent a promising avenue for expanding affordable housing options in a manner that is both economically viable and community-focused. By leveraging underutilized property space, ADUs offer a unique solution to the housing affordability crisis, one that benefits homeowners, renters, and communities alike. As more regions embrace the potential of ADUs, their role in shaping the future of affordable urban living continues to evolve, offering a glimpse of a more inclusive and accessible housing market.