Choosing the right construction material is pivotal in determining the efficiency, cost, and durability of a building. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs), Light Gauge Steel (LGS), and traditional wood framing are three popular choices, each with its distinct advantages and challenges. Here’s a comprehensive comparison including traditional wood framing to help you make an informed decision.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)
Pros:
- Energy Efficiency: SIPs have excellent insulation properties due to their foam core, significantly reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Quick Assembly: Pre-fabricated panels allow for faster construction, reducing labor time and costs.
- Strong and Durable: Offers high strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing the structural integrity and longevity.
- Tight Envelope: Minimizes air leakage, boosting energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
- Versatility: Can be used for walls, roofs, and floors, providing flexibility in use.
Cons:
- Higher Initial Cost: Generally more expensive upfront due to specialized materials and technology.
- Pest Concerns: Wood components may attract pests if not treated.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Requires careful sealing to prevent moisture ingress, which can lead to mold and structural issues.
- Modifications: Changes post-assembly can be difficult and costly.
- Specialized Labor: Requires contractors with specific expertise in SIP construction.
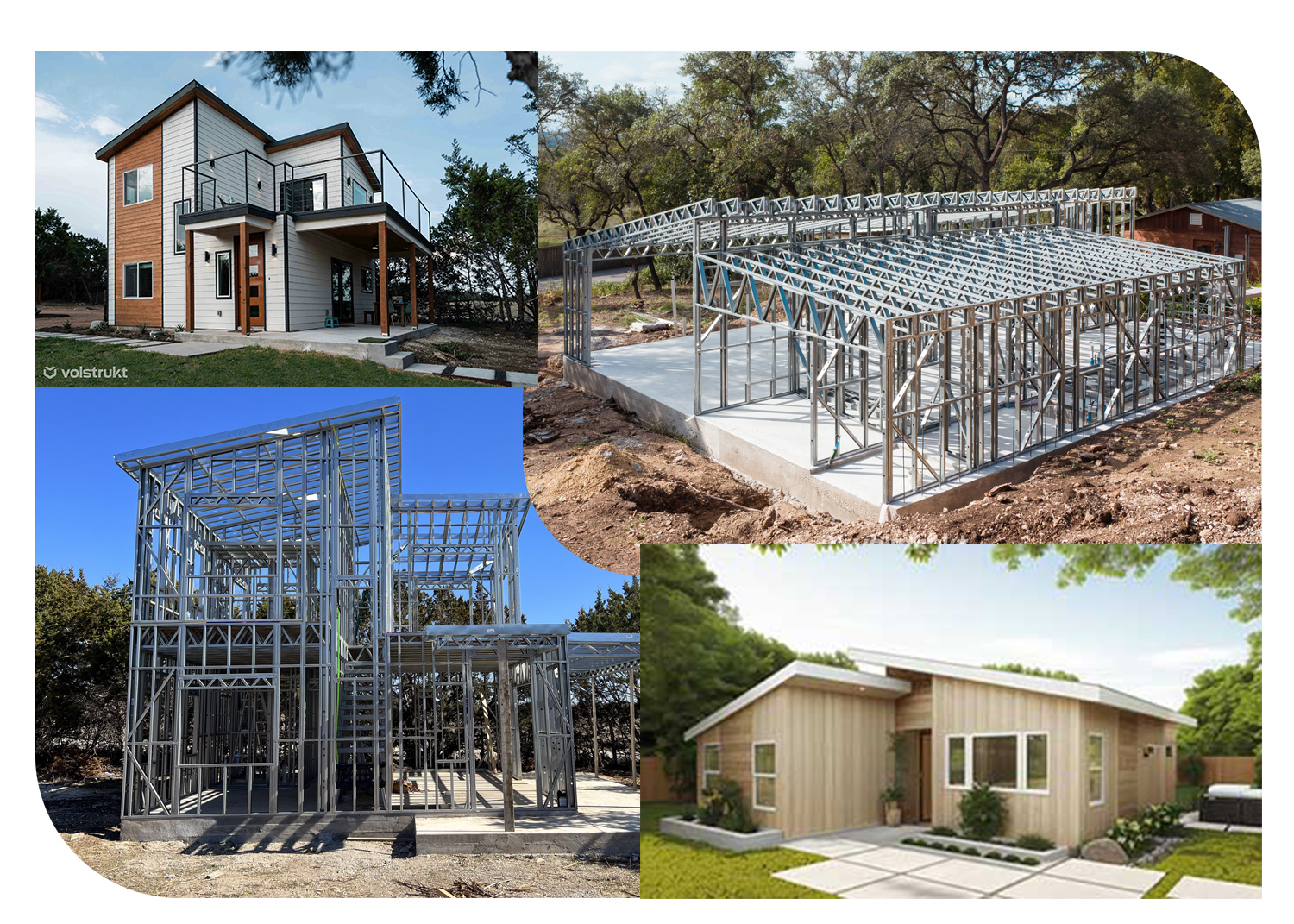
Light Gauge Steel (LGS)
Pros:
- Durability and Longevity: Highly resistant to rot, pests, and fire.
- Sustainability: Steel is fully recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
- Precision: Prefabrication leads to precise construction with minimal waste.
- Construction Speed: Allows for quicker on-site assembly.
- Load-bearing Strength: Ideal for regions with harsh weather conditions due to its robust nature.
Cons:
- Thermal Conductivity: High heat conduction requires additional insulation.
- Corrosion Risk: Vulnerable to corrosion if not properly maintained.
- Cost Fluctuations: Steel prices can vary significantly, affecting budgeting.
- Acoustic Transmission: Can transmit sound more readily unless acoustically treated.
- Expertise Requirement: Construction requires specialized skills.
Traditional Wood Framing
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than SIPs and LGS, both in material and labor costs.
- Flexibility in Design: Easier to modify and adapt during the construction process without requiring specialized tools or skills.
- Availability of Materials: Wood is widely available and does not require specialized manufacturing processes.
- Proven Track Record: Long history of use with well-understood properties and behaviors.
- Natural Insulation: Wood has natural insulative properties, though less effective than SIPs.
Cons:
- Maintenance: More susceptible to issues like rot, mold, and termite infestation, requiring preventive treatments and regular checks.
- Fire Risk: Wood is inherently more flammable than steel, posing a higher fire risk without proper treatment.
- Environmental Impact: Wood framing relies on timber, which raises concerns about deforestation and sustainability.
- Longevity: Generally has a shorter lifespan than steel or properly maintained SIPs due to its vulnerability to environmental factors.
- Variability: Natural material can vary in quality and strength, potentially affecting the uniformity and predictability of the build.
Conclusion
SIPs, LGS, and traditional wood framing each offer unique benefits and drawbacks. The choice between them should consider factors like budget, environmental conditions, project duration, and specific building needs. Whether you prioritize sustainability, cost, or construction speed, understanding these materials' properties will guide you to the best decision for your project.